Gum Disease Treatment
Advanced Treatments to Prevent Infection and Restore Healthy Gums
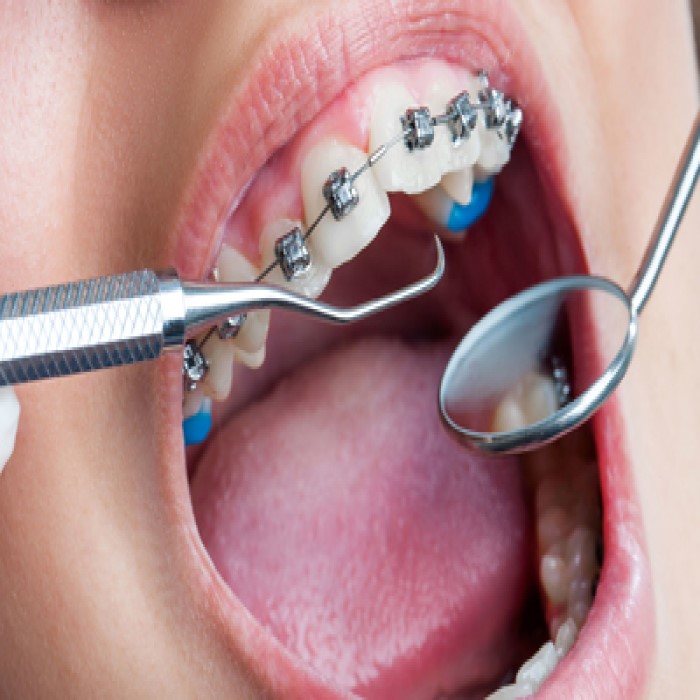
Gum Disease Treatment
Effective Care to Protect Your Gums and Maintain Oral Health
Periodontal disease is the leading cause of tooth loss worldwide. Fortunately, the best gum disease cure is prevention and early intervention. With ongoing preventative care and professional cleanings, the need for gum treatment is significantly reduced.
During your exam, we’ll use diagnostic X-rays and a special tool to measure the attachment levels of your gum and bone tissues around each tooth. Depending on the amount of structural loss or detachment there is, you will fall into a category of healthy gums, gingivitis, or mild, moderate, or severe periodontal disease
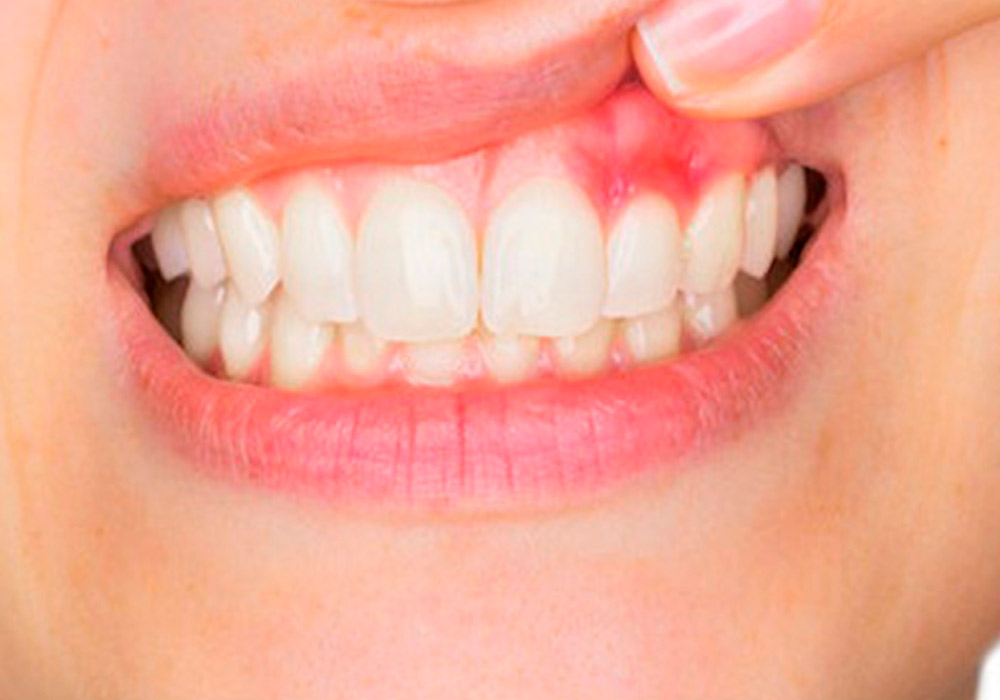
Gingivitis Treatment
The first phase of gum disease is gingivitis. Fortunately, gingivitis is fully reversible if caught early enough. Symptoms of minor irritation and redness are common. With good oral hygiene and professional cleanings, most cases of gingivitis can be reversed within two weeks
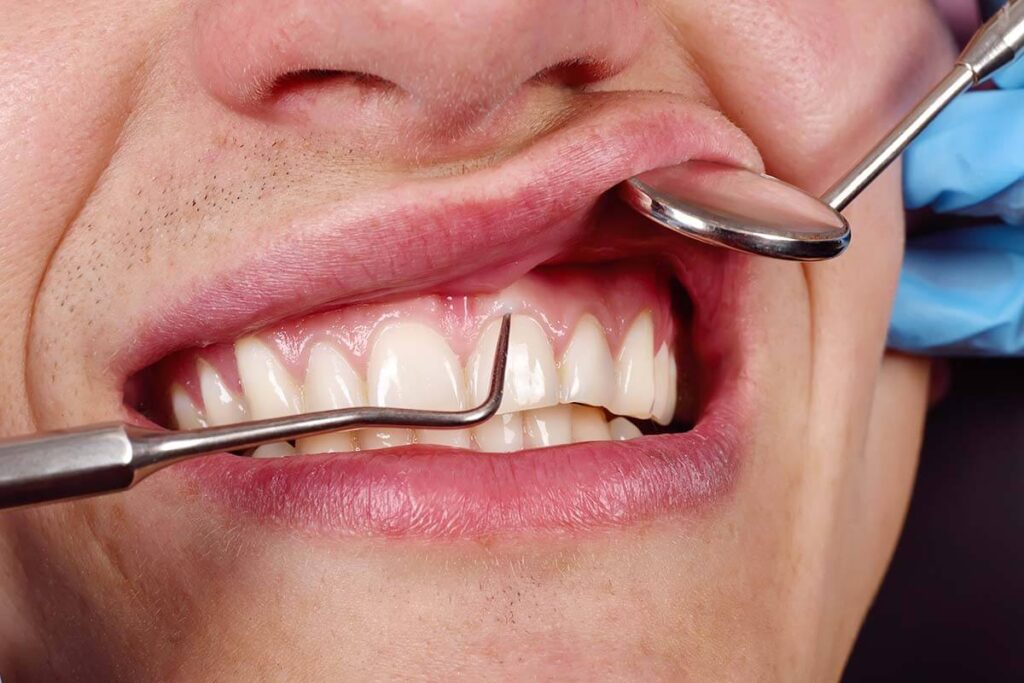
Periodontal Therapy
Untreated gingivitis will eventually progress into periodontal disease. At this point, the soft tissues around the teeth become infected and start to detach from the root surfaces. Bone shrinkage soon follows. As a result, deep “pockets” form between the gums and teeth where the detachment has occurred
Frequently Asked Questions
Work with our dentists to create a modified oral hygiene plan and series of professional cleanings to remove the bacteria responsible for your gum infection
- Typically, gingivitis is the result of poor oral hygiene. Especially a lack of flossing and brushing along the gums
Gingivitis is the inflammation of the gingiva (gums) around teeth. It is usually caused by bacterial plaque buildup around the teeth
Untreated gingivitis can advance to periodontitis. This causes gums to separate from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected. As the disease progresses, the pockets deepen and more gum tissue and bone are destroyed
- Bleeding gums
- Gum recession
- “Long teeth”
- Halitosis (chronic bad breath)
- Heavy tartar buildup
- Swollen, sensitive gums
- Spaces between teeth
- Food trapping between teeth
- Tooth mobility or loss

